System availability and service quality characterize technical field service. Maintenance strategies structure maintenance and service tasks and create a robust basis for plannable assignments in Field Service Management (FSM).
On this basis, the predictability, prioritization, and traceability of service assignments come to the fore. Maintenance strategies provide the organizational framework within which field service processes are controlled and further developed.
In the following, you will learn what maintenance strategies are and what role they play in FSM.
Maintenance strategies: Classification in technical service
Structural specifications describe how maintenance, repair, and servicing are organized. Maintenance strategies define when measures are triggered, which processes apply, and how results are documented.
Depending on their focus, these strategies are based on fixed intervals, condition values, or failure assumptions. In field service management, they serve as a technical framework for plannable service calls and traceable processes in the field.
Field Service Management – The Importance of Structured Maintenance Strategies
In the operational service environment, maintenance strategies determine when service orders are triggered and how they fit into existing processes. They thus create a technical basis on which planning and control are based.
Without this framework, priorities and processes lose clarity. Maintenance strategies ensure comprehensible deployment logic and support consistent structures in the organization of field service assignments.
They also influence issues such as route planning, capacity utilization, and response times. On this basis, services can be systematically evaluated and assessed using appropriate key performance indicators.
Maintenance strategies in the service environment
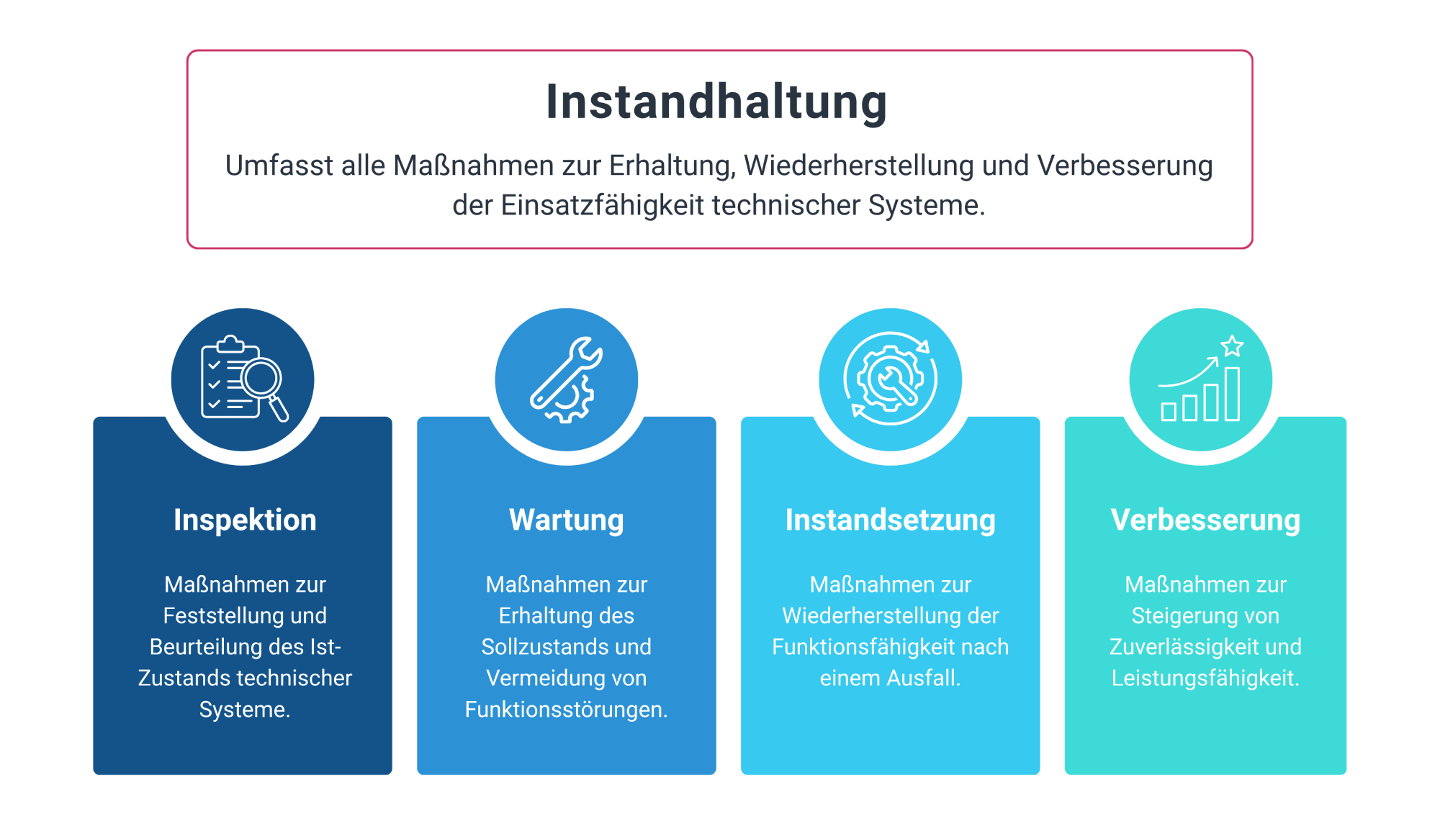
Different maintenance strategies determine when measures are initiated and how service calls are handled in the field. They create a structural framework for organizing maintenance, repair, and inspection in a comprehensible and predictable manner. The following strategies are among the most common approaches in practice.
Malfunctions lead to service calls after breakdowns. Maintenance measures only begin once a system is no longer available. In practice, this often means short-term scheduling, increased coordination requirements, and low predictability, as unplanned tasks are prioritized.
Time- or usage-based maintenance is based on fixed intervals or defined running times. This allows service calls to be planned in advance and integrated into existing routes. Regular maintenance ensures even workload distribution and stable processes in the field.
Measurements, status data, or limit values determine when maintenance is required. Service calls are based on the actual condition of a system rather than fixed schedules. This approach supports needs-based service calls and reduces unnecessary maintenance appointments.
Forecasting models and analyses enable early assessment of potential failures. Maintenance schedules can be derived from historical data and trends. This creates a reliable basis for forward-looking resource planning and coordinated resource utilization.
What makes a good maintenance strategy
Stable service processes are based on maintenance strategies that are geared toward real-world operations and remain viable in everyday use. The focus is on clear structures that support maintenance, service calls, and evaluation. The following points show which characteristics play a role in this.
Stable service processes thanks to well-thought-out maintenance strategies
See how Innosoft structures maintenance, resource planning, and key performance indicators. Get a no-obligation consultation now.
Maintenance strategies: Criteria for a suitable strategy
The selection of a suitable maintenance strategy can be prepared systematically. A short checklist that takes key influencing factors in service into account provides clear guidance. The following points show what to look for when making your selection.
Strengths and limitations – a direct comparison of maintenance strategies
Once the relevant criteria have been selected, a structured comparison helps to quickly identify the differences between the common maintenance strategies. The following table shows the strengths and limitations of each approach and the scenarios for which they are suitable:
| Maintenance Strategy | Advantages | Disadvantages | Suitable for |
| Reactive Maintenance | low planning effort, no regular maintenance costs |
unplanned downtime, high coordination effort in service |
non-critical assets, low impact of failures |
| Preventive Maintenance | predictable service activities, balanced workload |
maintenance independent of actual condition, potential over-maintenance |
standardized assets, stable operating conditions |
| Condition-Based Maintenance | demand-driven interventions, reduced unnecessary maintenance |
additional data collection effort, dependence on data quality |
technically monitorable assets, varying usage patterns |
| Predictive Maintenance | early planning, improved resource allocation |
high analytical effort, dependence on historical data |
complex assets, high availability requirements |
Typical problems when choosing maintenance strategies
Different framework conditions make it difficult to choose a suitable approach. Technical diversity, changing usage, and heterogeneous service requirements often lead to inconsistent decision-making criteria and make consistent implementation in everyday service difficult.
Limited data quality is another hurdle. Missing histories, incomplete documentation, or incomparable key figures reduce the informative value of fault and maintenance data and distort the evaluation of individual strategies.
Organizational factors also play a role. Divergent processes, different priorities in service, and a lack of transparency regarding resource availability mean that strategies appear viable in theory but are difficult to implement in the operational environment.
Making success measurable – KPIs for maintenance strategies
Key performance indicators provide concrete information on how viable a maintenance strategy is in everyday service. They form a measurable basis for classifying the planning, implementation, and results of maintenance and service processes. KPIs are collected continuously and allow for evaluation independent of individual assignments.
Typical KPIs in service for evaluating maintenance strategies include:
- System availability as a key figure for evaluating operating times and downtimes
- Mean time to repair (MTTR) for classifying response and processing times in service
- Frequency of use for analyzing maintenance and fault occurrence
- Maintenance costs in terms of time or resources used per measure
- First-time fix rate for evaluating the quality of maintenance and repair assignments
- Plan and schedule deviations for analyzing compliance with planned maintenance
- Costs per assignment for economic consideration of services
These key figures are characterized by comparability, repeatability, and clear assignability. They enable a structured evaluation of maintenance strategies and provide a reliable basis for their further development.
Structured maintenance strategies for predictable service calls
Learn how Innosoft provides clear support for maintenance, service planning, and evaluation. Get a no-obligation consultation now.
Digital support in everyday life – maintenance strategies in use
Maintenance strategies require a technical basis in everyday service in order to be implemented consistently. Digital systems help to translate strategic guidelines into operational processes. FSM software such as Innosoft exemplifies where software supports this process without dictating the strategy itself.
Structure in everyday service – the role of maintenance strategies
Finally, it becomes clear what influence maintenance strategies have on the organization and execution of service calls. They provide a comprehensible framework for maintenance and repair and support predictable control in technical service.
Their effect is particularly evident in stable processes, better coordination, and reliable decision-making bases. Digital systems such as FSM software from Innosoft support these structures by bundling information, clearly mapping processes, and enabling evaluations. In this way, service quality, efficiency, and cooperation in the field can be continuously developed.
Frequently asked questions about maintenance strategies
Maintenance strategies describe structured procedures for planning, implementing, and evaluating maintenance and repair measures. They specify when service calls take place, which triggers apply, and how measures are documented in order to manage plant availability and service processes in a traceable manner.
Maintenance strategies aim to ensure predictable plant availability and manage service calls in a structured manner. They support reliable maintenance planning, reduce unplanned downtime, and create a transparent basis for cost control, resource utilization, and service quality.
In practice, different types of strategies are used. These include reactive approaches after a failure, preventive maintenance at fixed intervals, condition-based strategies based on measured values, and predictive concepts that predict failures using data analysis. These approaches are often combined depending on the area of application.
The choice depends, among other things, on system criticality, intensity of use, available resources, and agreed service levels. Data availability, maintenance histories, and organizational conditions also play a role in determining suitable strategies.
Preventive maintenance is based on fixed time or usage intervals and enables maintenance to be planned effectively. Predictive strategies rely on status and history data to determine maintenance dates at an early stage. This allows service calls to be scheduled as needed and reduces unplanned downtime.