Maintenance management creates a clear structure for planned service calls and helps companies organize maintenance tasks and service orders in a clear and concise manner. It forms the basis for coordinated resource planning, in which teams, appointments, and objects are reliably coordinated with each other. In field service management (FSM) in particular, this approach helps to classify upcoming activities and keep track of recurring requirements.
Definition: What is maintenance management?
The structured planning and organization of maintenance tasks, service calls, and related objects forms the core of maintenance management. It encompasses all steps necessary to systematically record, schedule, and document recurring activities in technical service.
Essentially, maintenance management provides a clear framework in which maintenance activities, responsibilities, and processes are recorded transparently. This allows the entire service process to be clearly mapped from preparation to execution without going into detailed process steps.
Structured service processes: different types of maintenance management
Various approaches have become established in technical service, each with different triggers and objectives. Each type describes a unique approach to planning and executing maintenance activities. The following variants are among the most common fundamentals in maintenance management.
Reactive maintenance
Reactive maintenance is used as soon as a failure, malfunction, or clearly identifiable defect occurs. In such situations, the focus is on restoring the affected component in order to regain operational readiness as quickly as possible. This approach often involves spontaneous or time-critical interventions and is directly oriented toward an acute need that cannot be postponed. Reactive measures therefore play a central role, especially in the event of unexpected problems.
Predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance is based on a combination of data analysis, forecasts, and continuously recorded status information. The aim is to identify potential failures at an early stage and plan maintenance activities at precisely the point in time when they are most likely to be required. Digital monitoring systems, historical data, and analytical models provide indications of incipient wear or impending functional losses. This approach enables particularly precise determination of the optimal maintenance time and supports long-term planning.
Preventive maintenance
Preventive maintenance follows clearly defined intervals in which inspections, checks, and maintenance activities are carried out regularly. This form relies on fixed schedules to check components, devices, or systems at regular intervals and reliably cover known wear points. This is intended to prevent failures in advance. The structured rhythm creates predictability and ensures that recurring activities remain in focus without having to react to short-term events.
Condition-based maintenance
Condition-based maintenance is based on the actual condition of a device or object. Measurements, inspections, and sensory data provide indications of when intervention is advisable or necessary. This type of maintenance is based on the observation of actual wear and tear, which can deviate significantly from the specified interval rhythm. By basing planning on objective data, maintenance can be tailored to actual requirements, which both conserves resources and avoids unnecessary interventions.
Importance in everyday service – why maintenance management plays a role
A well-structured approach to technical service helps to reliably plan maintenance activities and map recurring tasks in a traceable manner. A clear overview of service calls, resources, and relevant objects makes it easier to prioritize upcoming work in a meaningful way and prepare processes in an orderly manner.
This framework allows those responsible to keep track of both regular inspections and short-term requirements. Maintenance management thus creates the basis for clearly controlling technical services and transparently classifying all steps involved, without going into specific processes or methods at this point.
Plan and document maintenance activities safely
With a digital solution, you can keep track of service orders, appointments, and feedback. Innosoft provides the structure to clearly map maintenance processes and manage them efficiently.
Factors that make maintenance management challenging
In technical service, numerous operational conditions interact, requiring a clear structure for handling maintenance activities. Different plant environments, changing operating situations, and diverse technical requirements mean that planning and coordination processes in everyday service must be organized very carefully. The large amount of information that needs to be taken into account requires orderly processing to keep processes clear.
At the same time, capacity and schedule coordination play an important role, as both planned activities and unforeseen tasks must be brought into a coherent overall picture. In addition, regularly occurring inspections and documentation-related steps require a consistent structure so that the ongoing service process can be reliably supported on a permanent basis.
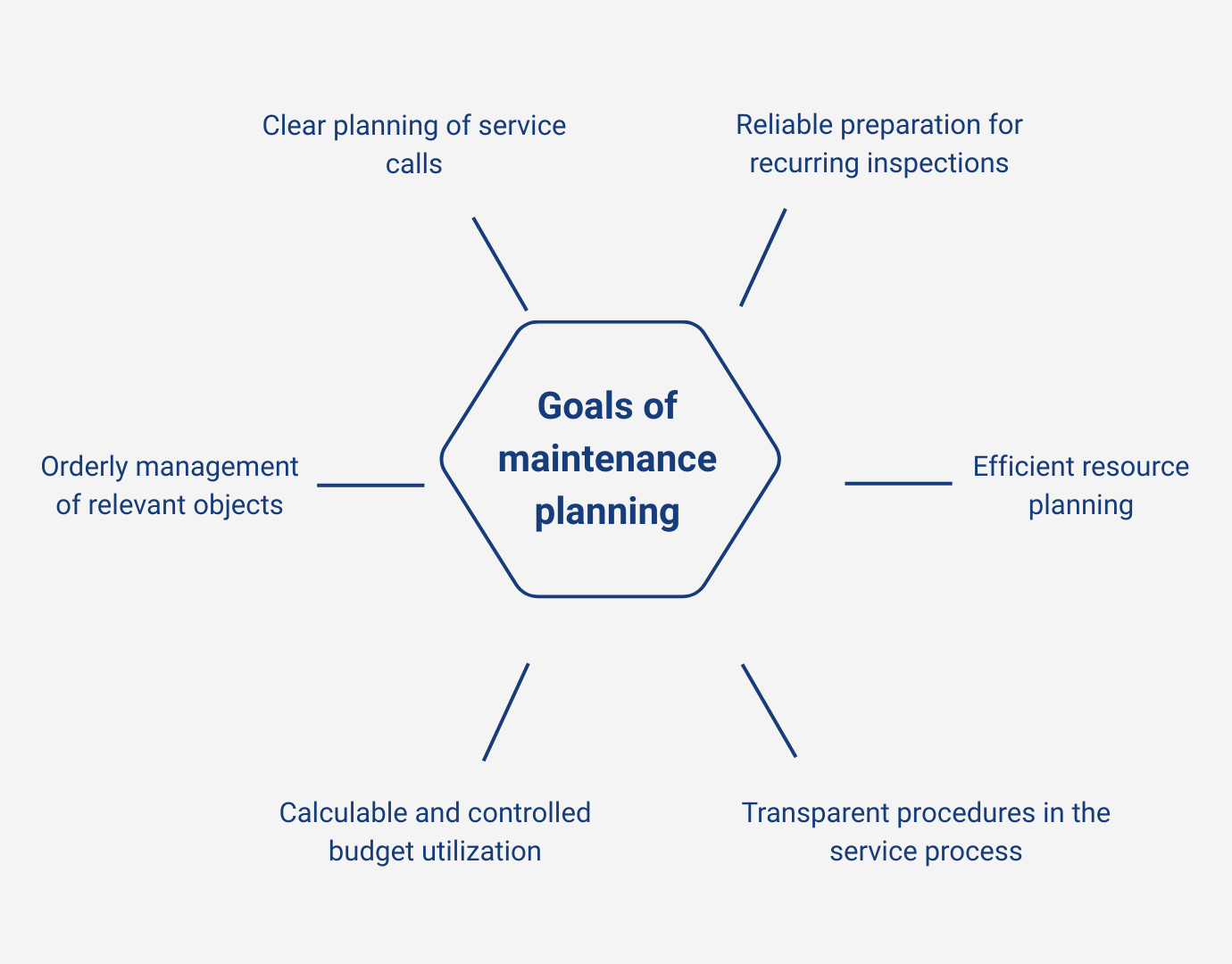
Clear focus in service – maintenance planning objectives
A clear focus within technical service processes pursues several objectives that reliably structure maintenance activities and make recurring processes transparent. The focus is on planning that sensibly coordinates tasks, responsibilities, and resources. The following points provide an overview of the key objectives.
Maintenance management in action: typical areas in technical service
Different areas rely on structured organization of technical services, as maintenance activities play a central role in field service management. The following areas of application illustrate the environments in which a clearly structured approach can be supported and recurring tasks can be mapped in an orderly manner:
- Facility management
- Municipal facilities and public utilities
- Service companies with field service
- Real estate and property management
- Utilities and infrastructure companies
- Technical service areas with regular inspection requirements
Efficient everyday service – advantages of organized maintenance management
A clearly structured technical service organization helps companies to map maintenance activities in a predictable and transparent manner. Fixed processes make it easier to classify recurring tasks, which simplifies both resource planning and documentation. At the same time, field service management teams benefit from a clearly structured overview that clearly assigns responsibilities and resources. The following points highlight the key advantages of a structured approach:
Create a structure for your technical service
Digital planning, centralized data storage, and mobile data entry improve the overview of all maintenance activities. Innosoft supports you in the smooth organization of your service calls.
Complexity in technical service: typical challenges
Many technical service processes are characterized by changing service requirements and complex planning conditions in the field. Different sources of information and varying organizational structures make coordination and consultation between multiple parties particularly challenging. This increases the effort required for field service management and necessitates careful preparation of all steps.
An additional challenge is often incomplete data and documentation, which makes reliable planning difficult. Missing or incomplete information influences the assessment of upcoming activities and impairs the overview of the current maintenance status. At the same time, short-term service calls in the event of a malfunction must be reconciled with regularly recurring tasks, which makes structuring the overall process complex. This shows how diverse the requirements in maintenance management can be, without anticipating specific solutions at this point.
Efficient processes – digital support in field service
Digital solutions help technical service teams to map maintenance activities in a structured way and bundle key information clearly. Modern FSM software such as Innosoft creates clear processes, simplifies planning, and ensures that service calls, object information, and feedback are available at all times. Maintenance management software can offer the following advantages, especially in field service management:
Digital maintenance management: structured planning with Innosoft
Modern planning in technical service benefits from systems that centrally collect information and clearly structure processes. In field service management, Innosoft offers a digital basis for clearly coordinating maintenance and service assignments and flexibly adapting them to current requirements.
Software-supported organization allows appointments, resources, and order information to be precisely coordinated. Activities are documented transparently, making preparation and execution much easier to track. The result is a structured way of working that reduces administrative effort and sustainably improves service quality.
Interested in a digital solution for your maintenance management? We would be happy to show you how Innosoft supports your service processes and makes field service assignments more efficient to plan.
FAQ – Maintenance Management in Field Service Management
Maintenance management encompasses the structured planning, organization, and documentation of maintenance activities in technical service. It ensures that regular inspections, service calls, and recurring tasks are prepared and executed in a traceable manner. The goal is a transparent and orderly way of working that reliably maps all relevant information.
Four basic approaches have become established in maintenance management:
- Reactive maintenance, which is only carried out after a defect has occurred
- Preventive maintenance, which is based on fixed intervals
- Condition-based maintenance, which is based on the actual condition
- Predictive maintenance, which uses forecasts and data analyses to determine the optimal time for intervention
Maintenance typically includes inspections, cleaning, functional tests, adjustments, and the replacement of wear parts. In addition, all steps are documented so that the condition of the respective object remains traceable and subsequent measures can be based on reliable information.
Digital systems bundle all relevant maintenance and service data in a central platform. They support resource planning, manage maintenance histories, provide mobile information for technicians, and coordinate all steps from order to documentation. This allows field service management processes to be clearly mapped and controlled more precisely.